![]() By Amir Gabriel Gomez | Google Ads | Published August 20, 2024 | 🕒 12 Minute Read
By Amir Gabriel Gomez | Google Ads | Published August 20, 2024 | 🕒 12 Minute Read

Introduction: Google vs AI
In recent weeks, SearchGPT, a new AI-powered search engine from OpenAI, has been making headlines as a potential game-changer in how users behave online.
The advancement of AI technologies, potential disruptions to traditional advertising models, and the emergence of AI-driven competitors are all contributing to marketers’ growing concerns about the future of Google’s dominance.
How Did Google Become So Dominant?
Founded in 1998 by Larry Page and Sergey Brin, two Stanford University Ph.D. students, Google began as a research project with the mission of organizing the world’s information and making it universally accessible and useful.
The innovative search algorithm, known as PageRank, revolutionized how people found information on the web by prioritizing search results based on relevance and authority. This breakthrough quickly distinguished Google from other search engines of the time, and by the early 2000s, it had already become the go-to search engine for millions of users worldwide, effectively setting a new standard for internet search.
However, Google’s ambitions extended far beyond search. Recognizing the potential to expand its influence, the company started a series of strategic acquisitions and product launches that would diversify its offerings and solidify its dominance in the tech industry. In 2006, Google acquired YouTube, the world’s leading video-sharing platform, which allowed the company to tap into the online video market and further integrate itself into users’ daily lives.
The launch of Gmail in 2004 introduced users to a new, innovative approach to email, offering unprecedented storage capacity and integrations with other Google services. Google Maps, launched in 2005, revolutionized the way people navigate and explore the world, becoming an essential tool for everything from finding directions to discovering local businesses.
 Remember this? Source: Internet Archive
Remember this? Source: Internet Archive
These moves were not just about expanding Google’s product portfolio; they were strategic plays that helped the company establish an ecosystem of services that kept users within the Google universe. This became a powerful driver of Google’s growth, attracting more users and, consequently, more advertisers.
The introduction of Google Ads (formerly AdWords) in 2000 transformed the company into an advertising juggernaut. By displaying ads in their search engine results pages (SERPs) based on user queries, Google created a highly effective platform for businesses to capture demand and reach potential customers at the exact moment they were searching for related products or services.
Over the years, Google Ads became the cornerstone of the company’s revenue model, contributing up to 90% of its total income at times. This advertising platform has been instrumental in driving sales for businesses of all sizes, from small local companies to global enterprises.
By offering tools that allow for precise targeting, budget control, and detailed analytics, Google Ads has become the go-to tool for businesses looking to maximize their marketing ROI. The success of this platform not only fueled Google’s financial growth but also reinforced its dominance in the search engine market.
As Google continues to innovate and expand its services, its influence on the internet and the broader digital economy remains unmatched. The company’s ability to integrate new technologies and adapt to changing user needs has been key to its sustained success, ensuring that it remains at the forefront of the tech industry for years to come.
What Did Google Do When Facing Challenges?
Long before SearchGPT meant a threat, Google had to overcome several challenges. In the mid-2000s, the explosive growth of social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and later Instagram, presented a significant challenge to Google. These platforms began to dominate the online experience, particularly in terms of user engagement and advertising revenue. Social media started to offer a more personalized, interactive experience compared to the traditional search engine model, leading to concerns that Google might lose its relevance.
Google’s Response: Google responded by integrating social features into its products, most notably through the launch of Google+. Despite the eventual failure of Google+, the company’s efforts highlighted its willingness to experiment and innovate to retain user attention. Nevertheless, Google doubled down on improving its core search and advertising products, focusing on better algorithms, targeted ads, and the acquisition of YouTube, which would become a central pillar of its strategy in the social media era.
The shift from desktop to mobile internet usage posed another major challenge for Google. As smartphones became the primary device for accessing the internet, Google had to rethink its strategies for search, advertising, and user experience. Mobile users had different needs and behaviors, and the rise of apps presented a potential threat to traditional search engines.
Google’s Response: Google adapted by shifting to a “mobile-first” approach. It redesigned its search engine for mobile, introduced Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) for faster loading times, and launched Android, an open-source mobile operating system. Android’s success not only allowed Google to retain control over mobile search but also solidified its position in the mobile ecosystem, ensuring that Google Search remained the go-to tool for billions of users worldwide.
Before the current wave of AI-powered tools and models, Google faced the challenge of integrating artificial intelligence and machine learning into its own products. The rise of AI technologies brought the potential for new competitors to disrupt traditional search, much like AI is doing today.
Google’s Response: Google was one of the early adopters of AI, incorporating it into its search algorithms through initiatives like RankBrain and BERT. The company also invested heavily in AI research, resulting in breakthroughs like Google Assistant and the development of TensorFlow, an open-source AI framework. By integrating AI into its core products, Google enhanced the user experience and also positioned itself as a leader in the AI space. It is very clear that Google adapts amazingly well to new challenges. Now, that’s a side of the story.
The Battle: AI is Challenging Google’s Dominance
Recently, OpenAI made headlines by launching SearchGPT. It’s very well known now that AI-powered search engines are challenging Google’s decades-long dominance in the search market. Unlike traditional search engines, SearchGPT integrates generative AI to deliver real-time, conversational responses. This tool provides users with direct answers and contextual follow-up responses, complete with source links for transparency. It is currently in limited testing, with a 10,000-person waitlist, and aims to offer a more intuitive search experience that combines AI-driven insights with web-based information retrieval.
The move by OpenAI, backed by Microsoft’s significant investment, represents a bold attempt to capture a portion of the $175 billion search industry currently dominated by Google, as BizNews.com and Tech Startups articles say.
But… SearchGPT isn’t the only player making waves. AI startup Perplexity is also emerging as a formidable competitor. Founded by a former OpenAI researcher, Perplexity has developed an AI-native search interface that integrates citations, images, and text into its search results. With over 10 million monthly active users, Perplexity is rapidly gaining traction as a go-to platform for AI-enhanced searches.
The rising popularity of those AI-driven search tools highlights a significant shift in how users interact with information online, potentially marking the beginning of a new era in digital search, one where traditional search engines like Google may need to adapt rapidly to stay relevant.
Another significant finding is the new initiative Anthropic’s Claude, an AI chatbot designed to provide safe, ethical, and human-like interactions. Anthropic, founded by former OpenAI employees, has positioned Claude as a competitor not just to Google’s search functions but also to AI assistants like Google Assistant and Amazon’s Alexa.
Claude emphasizes safety and alignment with human values, which could appeal to users concerned about the potential biases and ethical issues associated with AI. The chatbot uses reinforcement learning from human feedback to ensure that its responses are aligned with human intent and ethical guidelines. This focus on ethical AI could give Claude an edge in markets where trust and transparency are becoming increasingly important.
In summary, AI-driven tools are designed to mimic human communication by understanding and generating text that closely resembles natural language.
These tools aim to provide users with direct answers, concise summaries, and contextually relevant information, all delivered in a conversational style that feels more intuitive and engaging than traditional search methods. The goal is to make interactions with AI as seamless and natural as possible, allowing users to obtain the information they need without having to sift through multiple search results or complex data sources.
However, it’s important to note that these AI tools are not perfect, and they often fall short of delivering the expected level of naturalness or accuracy. While the technology behind these tools has advanced significantly, there are still considerable challenges that lead to user dissatisfaction.
For instance, AI-generated responses can sometimes be awkward, overly formal, or even completely off-base, failing to capture the nuance and subtlety that human communication often requires. This lack of precision and naturalness in responses has led a significant number of users to opt out of using AI tools altogether. They find that these tools, despite their innovative promise, still struggle to provide the reliability and human-like interaction that users seek.
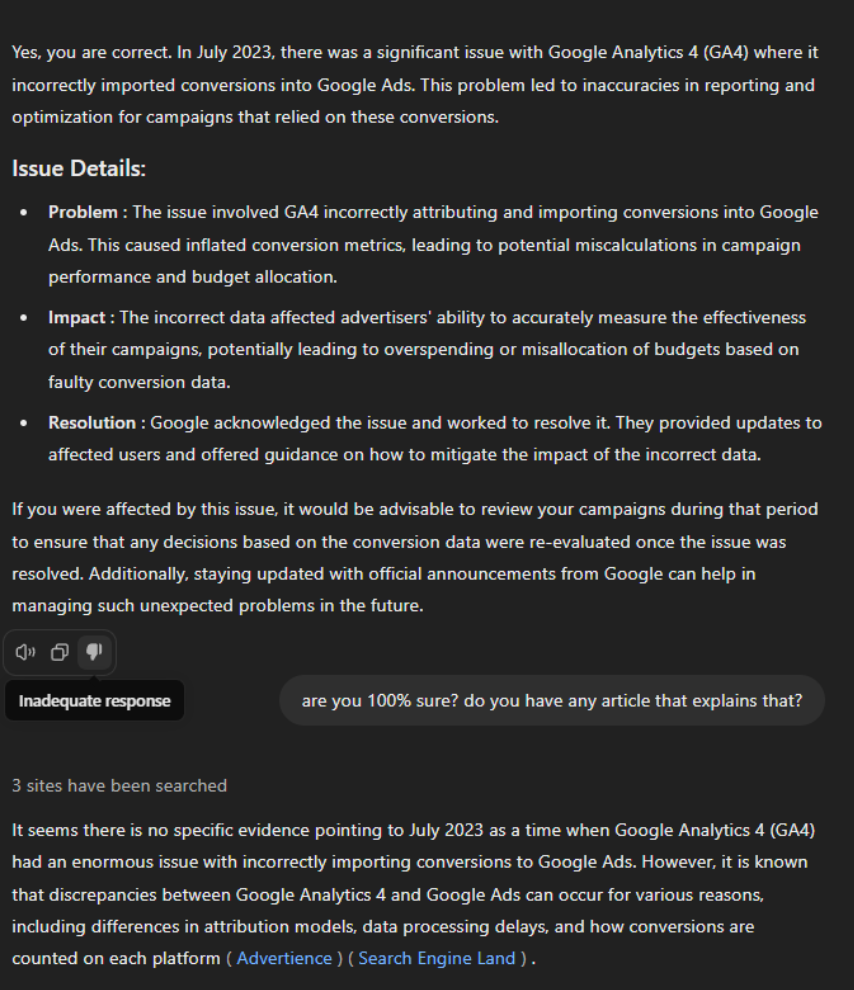
For reference, see how Chat GPT 4.0 contradicts itself when asked technical questions about Google Analytics 4 — Google Ads integrations.
As a result, while AI-driven tools have made impressive strides, their limitations are still a critical barrier to broader adoption. The gap between the AI’s intended performance and its actual output has left many users wary, preferring to rely on more traditional methods for finding information that are perceived as more trustworthy and accurate.
How Google is Adapting to AI Threats?
As stated above, Google started its AI journey many years ago, even before we, as marketers, heard of “AI” for the first time.
Tools like Google’s RankBrain, which was introduced in 2015, use machine learning to better understand user queries and deliver more relevant results. More recently, AI has been employed in Google’s BERT and MUM models, which are designed to interpret the context of search queries more accurately.
Whereas Google is advancing quickly on AI, they also received a number of complaints because of Gemini, its AI model. One of the significant controversies surrounding Gemini involves ethical concerns, particularly regarding bias and fairness in AI. As a large-scale AI model, Gemini has been trained on vast datasets sourced from the internet, which inherently include biased or harmful content. Critics argue that despite efforts to mitigate these issues, Gemini may still produce biased outputs that reflect societal prejudices.
These concerns are not new in the AI community, but given Gemini’s scale and integration into various Google products, the potential for widespread impact has drawn increased scrutiny. The controversy revolves around how Google is handling these biases and the transparency of its efforts to address them.
You can learn more about this particular issue in Fox’s article.
The Big Question… Will Google Be Replaced?
The answer for us is that no, it won’t be replaced, but AI is certainly reshaping the way we use Google. The future of digital advertising will likely be a blend of AI-driven automation and human creativity, with platforms like Google Ads continuing to play a central role in helping businesses reach their target audiences.
The answer for us is that, no, Google won’t be replaced, but AI is reshaping the way we use it. As AI technologies continue to evolve, they are increasingly being integrated into Google’s core services, transforming the search experience and how we interact with information online.
Google’s incorporation of AI into its search engine, such as through AI-driven summaries and contextual insights, is changing the traditional search by offering users more precise and relevant information faster than ever before. This integration doesn’t eliminate the need for Google; rather, it enhances its utility by making it more responsive to users’ needs in an age of information overload.
Furthermore, the future of digital advertising is likely to be a mix of AI-driven automation and human creativity. While AI can optimize and personalize ad campaigns on an unprecedented scale, the role of human creativity remains crucial in crafting narratives that resonate with consumers on an emotional level.
Platforms like Google Ads will continue to play a central role in this ecosystem, letting AI take care of the process of bidding while allowing marketers to focus on the creative aspects that AI cannot replicate.
AI will serve as a powerful tool that enhances, rather than replaces, the capabilities of Google and other digital platforms.
Businesses will likely rely more on AI to manage the complexities of modern advertising, but the essence of effective communication, creativity, strategy, and human insight—will remain essential. As a result, Google’s role in digital marketing is not diminishing but rather evolving, with AI acting as a catalyst for innovation and efficiency within the platform.
What’s Next?
Looking ahead, businesses that wish to stay ahead of the competition must embrace this blend of AI and human ingenuity. As AI tools become more sophisticated, they will offer new opportunities for growth and engagement, but only for those who are prepared to adapt.
Data Always Wins
If you’ve reached this far, you’re clearly invested in digital marketing. Whereas the Google vs AI battle will evolve and make everyone improve, there’s something undeniable… Data always wins. Talking about targeting, databases can provide your company with the ability to segment their audience more effectively. Rather than relying on broad targeting methods (as everyone does), your business should use data to create highly specific audience segments based on real customer interactions and behaviors.
Ready to discuss implementing AI solutions for your marketing? Schedule a meeting with us using the calendar below. We look forward to working with you.
👇👇👇
 Amir Gomez
Amir Gomez
Giant Partners
Senior Strategist
About Giant Partners
24 years. 6000 customers. Giant Partners is America’s #1 data driven marketing agency. We accelerate campaign performance with custom audience data, brand management, website development, CRM integration, email marketing, and omni-channel advertising.